 HOME > Research > Artificial Neuron and Network
HOME > Research > Artificial Neuron and Network
Artificial Neuron and Network
Artificial neuron and network research
- Current computers are developed mainly for calculations and are far ahead of the human brain in the mathematical area, but in terms of cognitive abilities, the human brain consumes thousands of times less power than the latest supercomputer-based artificial intelligence and shows higher accuracy. Neuromorphic computing refers to a computing system that operates like the human brain. Recently, studies have been conducted on the hardware-based implementation of neurons, synapses, and artificial neural networks using memristor characteristics.
1. Artificial neuron
1-1) Nociceptive memristor- The biomimetic characteristics of the memristor as an electronic synapse and neuron have inspired the advent of new information technology in neuromorphic computing. The application of the memristors can be extended to the artificial nerves on the condition of the presence of electronic receptors, which can transfer the external stimuli to the internal nerve system. In this work, nociceptor behaviors are demonstrated from the Pt/HfO2/TiN memristor for the electronic receptors. The device shows four specific nociceptive behaviors; threshold, relaxation, allodynia, and hyperalgesia, according to the strength, duration, and repetition rate of the external stimuli. Such nociceptive behaviors are attributed to the electron trapping/detrapping to/from the traps in the HfO2 layer, where the depth of trap energy level is ≈0.7 eV. Also, the built-in potential by the work function mismatch between the Pt and TiN electrodes induces time-dependent relaxation of trapped electrons, providing the appropriate relaxation behavior. The relaxation time can take from several milliseconds to tens of seconds, which corresponds to the time span of the decay of biosignal. The material-wise evaluation of the electronic nociceptor in comparison with other materials, which did not show the desired functionality, Pt/Ti/HfO2/TiN, reveals the importance of careful material design and fabrication.
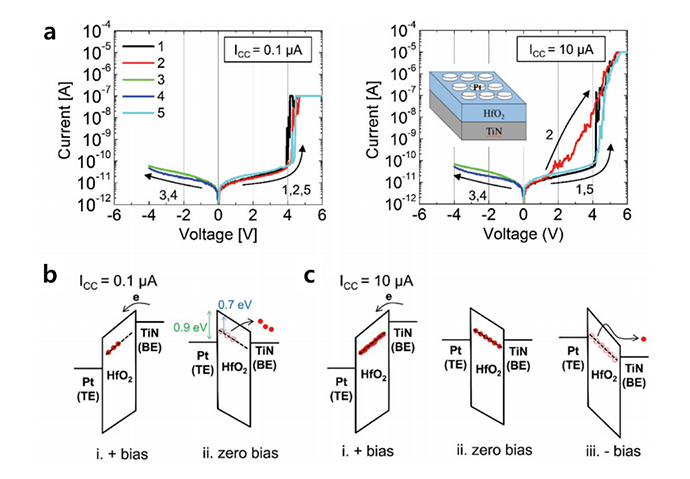
- Threshold and resistance switching behaviors in the PHT device, and the schematic band diagram. a) I-V curves obtained at the 0.1 µA (left panel) and 10 µA (right panel) ICC conditions. The right-panel inset schematically shows the device structure. Schematic band diagram of the device b) with a 0.1 µA ICC condition and c) with a 10 µA ICC condition.
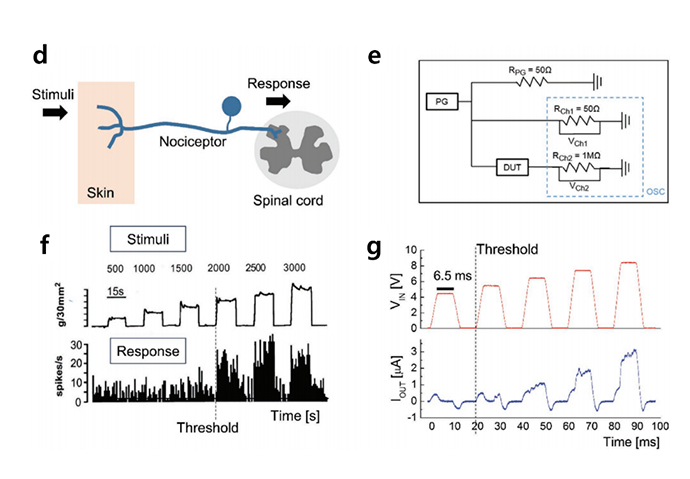
- Threshold characteristics of the nervous system and the PHT device. a) A schematic diagram of the typical nociceptor nervous system. The external stimuli are detected at the skin side end of the nociceptor, and the response signals are sent to the spinal cord (or the brain) through the opposite end of the nociceptor. b) One of the representative stimuli versus response results was obtained experimentally from a rat's nociceptive neuron. The data were reproduced with permission. Copyright 2014, Wiley-VCH. c) Circuit configuration for the electrical testing of the device. d) Input voltages applied by the pulse generator were monitored from Ch1 (upper panel), and output currents were monitored from Ch2 (lower panel).
Related Papers :
- Kim, Yumin, et al. "Nociceptive memristor." Advanced Materials 30.8 (2018): 1704320.
2. Neural network algorithm
2-1) eWB : Event-Based Weight binarization Algorithm for Spiking Neural Networks- A novel event-based weight binarization (eWB) algorithm for spiking neural networks with binary synaptic weight (-1, 1) based on the Lagrange Multiplier Method (LMM) is proposed. eWB algorithm features (i) event-based asymptotic weight binarization with only local data (ii) full compatibility with event-based learning algorithms such as STDP and event-driven random backpropagation (eRBP) (iii) the capability to address various constraints including binary weight constraint.
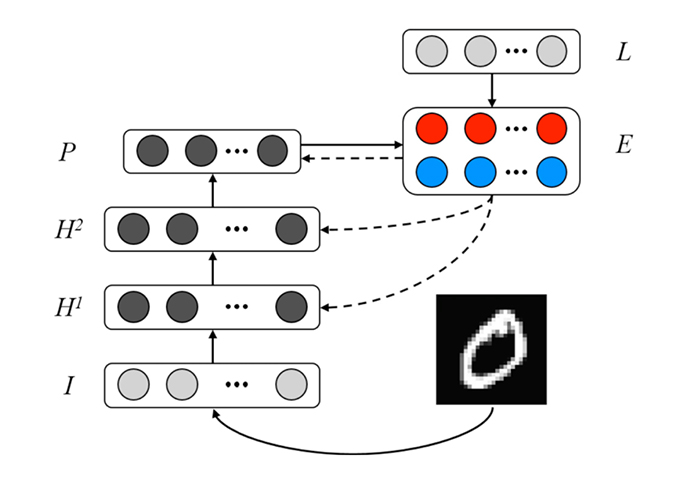
- Figure. A schematic of SNN architecture for eRBP. The error-coding layer (E) consists of two error-coding neurons for each label dimension that encode false positive and negative errors between labels (L) and prediction (P).
- During training, each of the hidden (H1 and H2) and prediction (P) neurons receives random feedback from the error neurons with fixed random weight. As proof of this concept, a single algorithm for learning binary weights combining eWB with eRBP (eWB-eRBP) for learning binary weights to generate correct classifications is proposed.
Related Papers :
- Kim, Dohun, et al. "ewb: Event-based weight binarization algorithm for spiking neural networks." IEEE Access 9 (2021): 38097-38106.
2-2) SPSNN : nth Order Sequence-Predicting Spiking Neural Network
- A method of harnessing spiking neural networks (SNNs) with rich dynamics as a dynamic hypothesis to learn complex sequences is proposed. The proposed SNN, named after nth order sequence-predicting SNN (n-SPSNN) is capable of single-step prediction and sequence-to-sequence prediction (associative recall). For n-SPSNN, a new algorithm named learning by backpropagating action potential (LbAP) is proposed, featuring (i) postsynaptic event-driven learning (ii) access to topological and temporal local data only (iii) competition-induced weight normalization effect (iv) fast learning.
- The key feature of the LbAP algorithm is that it offers a unified learning framework over the entire SNN only based on the local data. The prediction reaches its maximum (~1) when the number of hidden neurons (h) is greater than twice the training sequence length (l), i.e., h ≥2l. Another advantage is its high tolerance to an error in input encoding compared to the state-of-the-art sequence learning networks, namely long term-short memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit (GRU). Additionally, its efficiency is improved approximately 100 times than that of LSTM and GRU when measured in terms of the number of synaptic operations until successful training, which corresponds to multiply-accumulate (MAC) operations for LSTM and GRU. This high efficiency arises from the higher learning rate of the SPSNN, which is attributed to LDAP algorithm.
Related Papers :
- Kim, Dohun, et al. "SPSNN: Nth order sequence-predicting spiking neural network." IEEE Access 8 (2020): 110523-110534.
2-3) ANN for response inference of a nonvolatile resistance-switch array
- In response to a randomly applied voltage array to crossbar array (10×9 or 28×27) that employed an artificial neural network as a multilayer perceptron (MLP) leaky rectified linear unit, an artificial neural network (ANN) was utilized in the behavior inference of a random array of nonvolatile binary resistance-switch.
- This network was trained with 500k~1M examples, with an input feature in a vector form as conductance state distributions over a crossbar array labels, i.e. for M×N array where voltages are applied to its M rows, the input vector was M×(N+1) long. The calculated current vector for each crossbar array was used as the data labels for supervised learning.
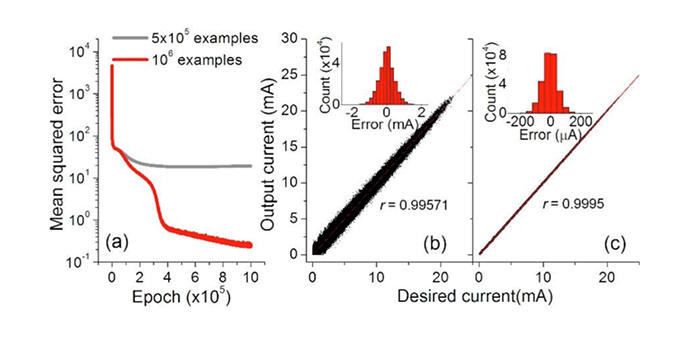
- Figure. Features training networks (2,500 units in each of two hidden layers) with 500k and 1M examples. As shown above, the correlation coefficient between inferred and true vectors reached 0.9995 for the larger crossbar array was obtained. This result highlights Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) that leverages its versatility to capture the quantitative linkage between input and output across the highly non-linear crossbar array.
2-4) Markov chain Hebbian learning algorithm with ternary synaptic units
- Despite the remarkable advances in machine learning technology, state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms require online training that keep machines from real-time learning, partially due to the computational complexity of parameter optimization. Alternatively, a learning algorithm for training memory in real-time has been proposed that is called a Markov chain Hebb learning algorithm.
- This algorithm features efficient use in memory during training in that (i) The weight matrix has ternary elements (-1, 0, 1) (ii) each update follows a Markov chain, i.e. no past weight values are required for the next update. This was validated by two proof-of-concept tasks: image recognition (MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets) and multiplication table memory. The latter performs multiplication operations based on memory which is analogous to arithmetic of human. These memory-based multiplication operations provide a feasible foundation for factorization and support new insights into memory-based operations.
Related Papers :
- Kim, Guhyun, et al. "Markov chain Hebbian learning algorithm with ternary synaptic units." IEEE Access 7 (2019): 10208-10223.
Related research group homepage
- Emerging Computing Lab. (hanyang.ac.kr) - Prof. Doo Seok Jeong
